· Webmaster Ayaselva · Medicinal plants · 4 min read
Tetrahydroharmine, another fascinating molecule found in the ayahuasca vines
Tetrahydroharmine enhances mood, cognition, with potential neuroprotective benefits
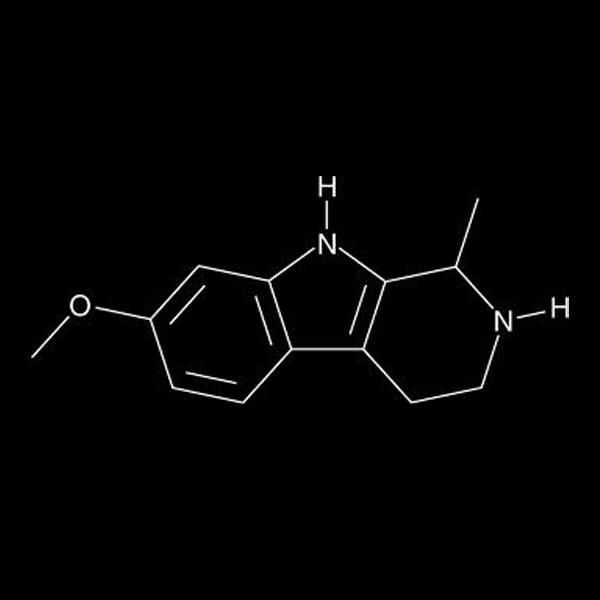
Tetrahydroharmine (THH) is an intriguing compound with a unique profile that has captured the interest of both scientists and enthusiasts. Found in certain plants, THH is a naturally occurring alkaloid that possesses a variety of properties, making it a subject of study and fascination. In this blog post, we will focus exclusively on tetrahydroharmine, exploring its origins, mechanisms of action, potential benefits, and current research.
Understanding tetrahydroharmine
Tetrahydroharmine is a member of the beta-carboline family, a group of compounds structurally related to tryptamines. These compounds are known for their effects on the brain, particularly their interactions with neurotransmitters. THH is one of the less well-known beta-carbolines but holds significant potential due to its unique characteristics.
Sources of tetrahydroharmine
Tetrahydroharmine is found in several plants, with the most notable source being the Banisteriopsis caapi vine. This vine is native to the Amazon rainforest and has been used for centuries in traditional practices. The concentration of THH in these plants can vary, and it is often extracted and used for its psychoactive properties.
Mechanism of action
Tetrahydroharmine works primarily by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase (MAO). This inhibition prevents the breakdown of monoamine neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. By blocking MAO, THH allows these neurotransmitters to remain active in the brain for longer periods, which can enhance mood and cognitive functions. Additionally, tetrahydroharmine may act as a mild agonist at serotonin receptors, directly stimulating these receptors to produce its psychoactive effects. This dual action—MAO inhibition and serotonin receptor activation—makes THH a compound of interest for its potential to influence mood and perception.
Potential Benefits of Tetrahydroharmine
The potential benefits of tetrahydroharmine are diverse and have been explored in both traditional contexts and modern research settings. One of the primary effects of THH is its ability to enhance mood. By increasing the levels of serotonin and other neurotransmitters, THH may help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. Users often report a sense of well-being and emotional clarity after consuming THH. Tetrahydroharmine may also improve cognitive functions such as memory, focus, and creativity. Its impact on neurotransmitter activity can enhance brain function, making it easier to concentrate and process information.
Neuroprotective properties
Some research suggests that THH may have neuroprotective effects, helping to protect brain cells from damage. This could be beneficial in preventing or slowing the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Anti-inflammatory Effects: Tetrahydroharmine has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties, which could be useful in treating conditions associated with inflammation, such as arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease.
Current research and future directions
Scientific interest in tetrahydroharmine has been growing, with researchers investigating its potential therapeutic uses. While much of the evidence remains anecdotal or based on traditional use, modern studies are beginning to shed light on the compound’s capabilities. In mental health, researchers are exploring THH’s potential as a treatment for depression and anxiety. Its ability to enhance mood and cognitive function makes it a candidate for further study in this area. Unlike traditional MAO inhibitors, THH is considered a reversible MAO-A inhibitor, which may offer a safer alternative with fewer side effects. There is also interest in understanding how THH might be used in neuroprotection. Studies are examining its effects on brain cells and how it might help in conditions like stroke or traumatic brain injury. The anti-inflammatory properties of THH are also being explored for their potential to treat various inflammatory conditions.
Conclusion
Tetrahydroharmine is a compound with a rich history and significant potential. Found primarily in the Banisteriopsis caapi vine, it has been used traditionally for its psychoactive properties and is now being explored for its therapeutic benefits. Its ability to inhibit MAO and act on serotonin receptors makes it a unique and valuable subject of study. While research is still in its early stages, THH shows promise in enhancing mood, cognitive function, and potentially offering neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory benefits. However, it is essential to use it with caution, respecting its powerful effects and potential risks. As scientific interest in natural compounds continues to grow, tetrahydroharmine stands out as a fascinating area of exploration. Whether for traditional use or modern therapeutic applications, THH offers a unique window into the complex interactions between natural compounds and the human brain.